by Greg Galluzzi
Since 2000, water utilities have been the dominant force in Customer Information System (CIS) selection and implementation market. Many water utilities elected to fix their legacy billing system for the year 2000 and had been running systems which were 20-30 years old. As a result, they were faced with billing systems which used old technology and were becoming difficult to support and enhance.
Industry analysts expect that the high level of CIS replacement activity that occurred within the water industry between 2000 and 2006 will continue at slightly lower levels in 2006 through 2010, with water utilities focusing on completing installation work and implementing phase 2 core and extended CIS components. Beginning in 2011 water utilities will revert to the low levels of activity characteristic of the 1980s and 1990s.
Application Plans
In today’s market, it is estimated that as many as 40% of utilities who are thinking about replacing their legacy billing systems are engaged in the development of an application plan.
Rather than rushing into a selection effort, the utilities are conducting a thorough assessment of their existing situation prior to issuing an RFP. They are engaged in the identification of business and technical requirements, assessment of their current environment, identification of industry trends, an evaluation of system alternatives and operational platforms, the development of a business plan, and the identification of next steps.
The development of an application plan provides the utility with a better understanding of CIS solutions and sets expectations regarding cost, timeframe, and resource requirements associated with the selection and installation of a new CIS.
Configure Vs Customize
Typically, once a water utility completes the application plan they engage in a 7 to 12 month CIS evaluation and selection effort to identify and procure a CIS package solution which can be implemented with minimal modifications and ongoing support provided by the CIS vendor. In fact, one of the biggest indicators of failure across CIS projects is when a utility tries to customize a CIS product rather than rely on configuration of the product. Many utilities who have implemented heavily customized CIS packages in recent years find themselves back in the market in order to implement a solution with minimal to no modifications.
The implementation of a “vanilla” CIS package allows the water utility to more easily take advantage of new vendor releases and versions of the CIS software. This is especially important if the utility expects the new CIS to function for another 20 to 30 years.
One of the primary objectives of any replacement effort is to select a vendor that will take the utility into the future. This means that about every 5 to 7 years the vendor will offer a new CIS solution with a migration path for its clients so they can easily upgrade to the new CIS. Without this CIS vision and long-term vendor viability the new CIS solution will stagnate and require replacement just like the legacy billing system.
Operational Platforms
There are several models for operating a customer information system, with various levels of outsourcing. Here are some examples:
1. In-house Solution. This alternative is provided as a baseline for comparison to the various outsourcing options. It represents an in-house custom or product solution which the utility is operating and managing internally without the help of a third party or vendor. Historically, this has been the most popular operational model.
2. Managed Application. The product vendor or a 3rd party assumes full responsibility for application maintenance & support, product releases, help desk, training, and consulting services. This model is the most popular outsourcing model as the utility retains physical control of the solution and its data.
3. Hosted Facility. A third party or application vendor assumes responsibility for the management and operation of a remote or local data center. The application continues to be supported by product vendors or in-house personnel. This model was popular in the late 1970s to mid-1980s and has realized a recent resurgence, making it the 2nd most popular outsourcing model.
4. Shared Services. Responsibility for application management and data center management is assigned to a 3rd party which may be: a third party vendor, an investor owned utility, a public owned utility, or other outside entities as identified. If the entity is an organization created by the utility to provide service to multiple subsidiaries it is known as a Shared Services environment. If an entity is external to the organization and is attempting to operate the solution for multiple energy utilities it is a co-sourced solution. The success of the co-sourced solution is spotty as it requires a significant investment in time to obtain agreement by multiple utilities on a CIS solution.
5. Outsourced Timeshare. The product is tailored to the specific needs of the utility and subsequently supported and operated from the outsourcer’s facility. Service is provided through the Internet, VPN, or other provider connectivity. Typically, the utility does not own a product license, it is simply renting the application.
6. Application Service Provider. The base product is accepted with customization only allowed through product setup and definition tables. In theory the customer is renting time on the application with access through the Internet with a very thin client required. For complex CIS solutions this model remains an elusive one. In reality vendors offer an Outsourced model and have named it an ASP solution.
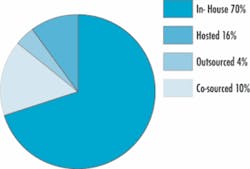
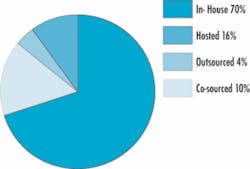
The majority of utilities, 70% in one industry survey, continue to operate the CIS solution within an in-house data center with the vendor managing the application. The hosted facility is quickly becoming the operational platform of choice growing to 16% of the survey sample. Co-sourced or shared services solutions make up 10% followed by the outsourced or ASP solution at only 4% of the survey sample.
Functional Assessment
If water utility management takes the time to analyze the functional capabilities of their current billing system they typically will find the system measures between a 20% to 60% functional fit when compared to an industry standard checklist. In comparison, a new CIS solution offers the water utility an 88% to 92% functional fit and includes capabilities such as: web-based systems; mobile computing; CRM-like capabilities; billing for non-utility operations; out-of-the-box integration with other applications; flexibility to quickly adapt to new products, programs, and services; and, ultimate support for the customer rather than just the premise or the meter.
The intent of a successful CIS project is to implement the core CIS functionality - focus on moving off the old system and onto the new system.
In addition to core functionality, a significant amount of extended functionality may be offered through other manual and automated systems which the water utility may either have in production or is planning to implement in the future. As a result, integration with these other “extended” applications becomes a real consideration and major success factor associated with any new CIS installation effort.
System Cost
A water utility can expect to spend the following on a new CIS solution:
- A utility will spend between $20 to $30 per customer metered service (PCMS) to vendors, consultants and integrators for core CIS hardware, software and services.
- The utility will spend another $10 to $30 PCMS on payroll costs and additional out-of-pocket costs for items such as overtime pay, bonuses, temporary staffing, project space, training facilities, etc.
- In addition, the utility may purchase additional hardware, software and services to implement extended CIS capabilities (e.g. change management, bill production, data warehouse). This cost is estimated at $0 to $30 PCMS for extended services and $0 to $20 PCMS for extended products.
- For example, a utility serving 100,000 customers with a single metered service can expect to spend up to $3 million on core, $3 million on staffing and out-of-pocket, and $5 million on extended, for a total of $11 million.
- To implement a core CIS without the use of a solution integrator the utility serving 100,000 customers will spend between $3 million and $5 million to implement.
- Ongoing annual maintenance varies between 18% and 24% of license (non-discounted) value.
A CIS replacement is one of the riskiest, costly, resource intensive projects a water utility will embark on. A number of utilities try one, two, and three times before they get it right. Hopefully, this article has provided some insight into this difficult and time consuming process.
About the Author:
Greg Galluzzi is the president and a senior consultant with TMG Consulting. He can be reached at [email protected].
Event to Focus on Utility CIS Market
CIS Week, an educational event for professionals involved in the customer service and customer information technology aspects of utility, cooperative and municipal management, has expanded its offerings to water utilities in many areas of the meter-to-cash lifecycle. Significant thought has gone into the agenda, particularly in the area of Automated Meter Infrastructure (AMI) and Meter Data Management (MDM). The total count of workshops has expanded to include 55 workshops targeting the electric, gas and water/wastewater utility industries. The event will be held the week of May 21 in Orlando, FL.
The CIS Executive Summit will address utility concerns that tend to keep senior executives up at night. Water utilities participated in this event for the first time last year and the Executive Summit promises to have a greater level of participation from water utilities this year. Discussions will include AMI/MDM, customer and employee privacy and compliance, and concepts around the ideal future CIS design. Another feature of this year’s Summit will be a workshop with noted customer service author Chip Bell. As in past years, the Summit offers utility executives a chance to find out how their counterparts are dealing with their most pressing issues.
CIS Synergy Groups were a new and popular feature of last year’s CIS Week. They will be back again this year. This forum allows users and technicians of the same customer system to meet with other users along with company representatives to discuss future enhancements and developments.
The CIS College has been approved by the National Association of State Boards of Accountancy (NASBA) as a registered sponsor on the National Registry of CPE Sponsors. Attendees may now receive CPE credits for each of the CIS College courses. In an effort to meet the immediate needs of so many, six CIS College courses are offered this year. Attendees will be able to find in-depth full-day classes covering: CIS selection and implementation; project management; call center development; outsourcing/multi-sourcing; and AMI-MDM.
CIS Week’s keynote speakers this year will include Captain James Lovell, the Commander for Apollo 13 in the first general session. He will share his wisdom and experience concerning the value of reliable technology and communication. On Wednesday, Dr. Chip Bell, a leading author specializing in customer loyalty, will challenge and motivate attendees as to how they do business today and what they need to do tomorrow to keep pace with offered services. John B. Ramil, President and COO for TECO Energy in Florida, will conclude the week with insights gleaned from 30 years of serving the public through TECO and its subsidiaries.
This year, CIS Week, WaterWorld and Electric Light & Power magazine have announced the newly formed 2007 Expanding Excellence Awards. These awards will recognize Excellence in Customer Service. This year has three awards: Best CIS Implementation Award; Innovation in Extending a Legacy Award; and Innovation in Customer Service Award. Winners will present overviews of their efforts and outcomes in a special workshop during CIS Week.
The CIS Week 2007 Exhibit Hall will showcase the best of what is new and proven in the customer information system market. Over 100 vendors and service providers will have software and solutions available for review. Aside from regular Exhibit Hall hours, special times have been designated for “Invitation-Only” demonstrations which provide opportunities for attendees to explore and learn from industry experts as they share their product and service information and recommendations.
For further information review the CIS Week web site at www.cisweek.org.