Diamond-based technology purifies water without chemicals
An innovative system developed by a Swiss research and development centre that uses diamond-coating technology to treat industrial wastewater and disinfect freshwater without using any chemicals.
In recent years, the Swiss Center for Electronics and Microtechnology (CSEM) established research activities in the field of environmental technology and developed new methods for water treatment without the use of chemicals and procedures to simplify water quality monitoring.
The company developed a diamond electrode-based system for water purification, the DiaCell®, that was selected by the European Environmental Press (EEP) as one of the ten EEP Award nominees for the “Environmental Innovation for Europe 2004.” These new developments are based on highly efficient electrolysis technology implementing CSEM expertise from electrochemistry, material science and microtechnology, sensor technology and engineering.
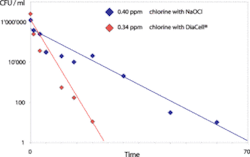
The majority of currently applied methods for water treatment use considerable quantities of chemicals to produce clean drinking and process water or for treating wastewater. The new water treatment technique developed at CSEM uses diamond coating technologies. This precious material is used in the electrolysis process as a self-cleaning electrode that supports the treatment of industrial wastewater and the disinfection of fresh water by reducing the chemical oxygen demand (COD).
The new technique is based on the latest knowledge in electrochemistry, since the chemical reactions take place within the micrometric range of reactive interfaces. Given the corresponding charge carrier interactions on special electrically charged surfaces, water is split into hydroxyl radicals, destroying any impurities, such as germs and dirt particles. A further advantage of this technique is that electrodes are installed inside the compact modular DiaCell system, which demands little space and low energy.
The DiaCell concept was initially developed for water disinfection in private swimming pools and was later proven to be suitable for many other applications because electrodes can be provided in different configurations. Each configuration leads to a different type of electrolytic process and, therefore, various applications. The electrodes are based on boron-doped diamond (BDD), which is a nano-polycrystalline coating on silicon plates. They are typically used to generate persistent oxidants for disinfection of drinking water or process water. Further potential for this technology is the inactivation of Legionella. The systems are able to destroy organic pollutants, even those that are non-biodegradable. The DiaCell system is used in the treatment of industrial effluents, organic matter oxidation and pollutant removal. Furthermore, the DiaCell systems allow the oxidation of inorganic pollutants, such as cyanides and hypophosphites, which is relevant for the regeneration of plating baths.
Its compact design and high efficiency makes the DiaCell system suitable for laboratory or industrial use, and for the disinfection of private swimming pools. More than 50 of these systems have already been installed worldwide, demonstrating the efficiency and eco-friendliness of this technology.
CSEM plans to create a start-up company, Adamant Technologies, to market these new technologies and products based on diamond coatings in addition to new methods for monitoring water quality.
Continuous monitoring of water quality is not only required for immediate action after contamination, but also to steer and observe the functioning of water treatment systems. Therefore, CSEM has devised new technologies that allow online monitoring of water quality. Highly sensitive microelectrodes together with their dedicated SenSysTM-Control units measure individual substances directly in the water and report the results to predefined points. Special analysis software enables an online determination of the concentrations of disinfectants such as chlorine, ozone and H2O2. Further solutions for the monitoring of parameters, such as O2, Cr, SO4, and S2O8, are currently being developed.
Author’s Note
The CSEM Section Head of Environmental Systems, Philippe Rychen, is based in Neuchâtel, Switzerland. For more information, contact the author at email: [email protected] or visit the website: www.csem.ch.