Reservoir Management System Improves Water Quality, Reduces Costs in Moulton Niguel Water District
By Larry Dees
Ever since the turn of the century, chlorine has been used in municipal water treatment systems to help provide a safe and sanitary drinking supply. But maintaining uniform levels of chlorine has long been a challenge for water system operators. Stagnation and stratification in reservoirs, insufficient feeding and blending, and ineffective analysis techniques often lead to chlorine levels that are either too high or too low.
At the Moulton Niguel Water District (MNWD) in south Orange County, CA, a reservoir management system developed by Severn Trent Services has resulted in more consistent, uniform chlorine residuals, improving water quality and reducing maintenance requirements and costs.
Conventional Methods
MNWD's 28 reservoirs serve approximately 160,000 residential customers. Water is purchased and delivered to reservoirs throughout the district via turn-outs of two major transmission mains. By the time the water reaches the reservoirs, it may contain unacceptable nitrification levels with little disinfectant. Without proper rechlorination, biofilm can grow in the reservoirs and bacteria can grow in the distribution lines. This can necessitate frequent flushing of the system to prevent nitrification, along with manual chlorination.
Attempts to solve this problem included filling reservoirs to less than half capacity to increase cycling frequency and prevent thermal stratification, and continuously monitoring the chlorine residuals. When residuals fell too low, chlorination equipment was transported to the appropriate site, and chlorine was manually added through a pipe connection at the top of the tank.
This solution proved unsatisfactory for several reasons. First, transporting bulk chlorine on crowded highways has become a major safety issue that is now stringently regulated by federal and local authorities. Secondly, the addition of chlorine alone is not adequate to properly reestablish an effective chlorine residual. Furthermore, it can also be extremely inaccurate and time consuming.
The natural effect of increased water temperature can cause warmer water to form a stagnant layer at the top of the reservoir, resulting in poor water quality in the reservoir and potential distribution issues. With a common inlet/outlet pipe connection at the bottom of the reservoir, the ebb and flow of water results in an unpredictable residual in the lower part of the tank, as well as a slug of stagnant water that can rise and fall.
Reservoir Management System
The first solution investigated involved installing a paddle wheel, propeller-type mixer to recirculate water throughout the tank. However, this system was prohibitive in cost and required a great deal of electricity. The district then investigated Severn Trent Services' ClorTec Reservoir Management System (RMS), and found it to be effective and lower in cost.
Designed to achieve a consistent, desired level of chloramine residual throughout the entire tank, the RMS system was initially installed during the winter of 2000 at the four million gallon Nellie Gail Reservoir. No downtime was needed to put the system in place.
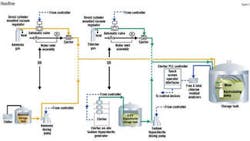
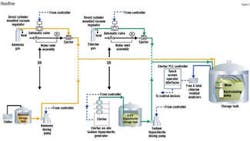
Operation of the system relies on a submersible pump installed through the roof of the tank and suspended about three feet from its floor, combined with an eductor nozzle on the pump effluent. Working together, these two components create a significant upflow of water, thoroughly mixing the tank's contents and eliminating thermal and residual stratification.
The system also includes free and total chlorine residual analyzers designed to measure chlorine levels throughout the tank. If either analyzer senses a deviation from setpoint, a dedicated PLC-based control calls for the injection of ammonia and/ or hypochlorite via conventional chemical metering pumps until proper chloramine residuals are restored. The circulation pump runs continuously, providing a fresh sample stream to the analyzer while continuing to blend the various flows in the reservoirs. The PLC-based control communicates all system operating parameters, residuals, etc., directly to the district's SCADA system where data is trended and analyzed.
Severn Trent also installed an on-site hypochlorite generator to produce 0.8 percent sodium hypochlorite at the Nellie Gail site, effectively eliminating the need for chemical transport and handling. Enough sodium hypochlorite solution is produced and stored to meet one or two day's requirements at maximum operating capacity.
Results
Results of the RMS system have proven significant. Improved mixing and real-time chlorine analysis have allowed the district to maintain a more homogenous water quality with consistent chlorine residuals throughout the tank.
The system also enables the reservoirs to be operated at higher levels, making more effective use of available capacity. When installed district wide, the RMS technology and capital equipment will provide the equivalent of three additional five million gallon reservoirs and one additional two million gallon storage tank, effectively eliminating the need to construct additional reservoirs, and saving substantial capital investment.
Because nitrification is no longer a problem, the new system also dramatically reduces the need for flushing. This does more than reduce labor and its associated costs; it also eliminates the public perception that the district is wasting water. This is also enhanced by the closed loop, reagentless nature of the analysis process, since all analyzed samples are returned to the tank for reuse.
Conclusion
Thanks to the success of the six-month pilot program, the ClorTec Reservoir Management System is now being adopted throughout the Moulton Niguel District. Phase I includes installations at eight sites involving 12 reservoirs. The remainder of the district will be converted during Phase II. All installations will be turn-key projects, and will include on-site chlorine generation, ammonia refrigeration and storage, PLC-based control systems with operator interface, free-chlorine residual analyzers, total chlorine residual analyzers, chemical metering pumps, submersible pumps and eductor assemblies, recorders, and associated valves and tank level controls.
About the Author:
Larry Dees is Director of Operations for the Moulton Niguel Water District, Laguna Niguel, CA.