Optimizing cement manufacturing for water treatment
TEXAS -- Researchers have found the right formula for mixing a cement that does double duty as a structural material and a passive photocatalytic water purifier with a built-in means of replenishment: simply sand down the material's surface to refresh the photocatalytic quality.
They found this recipe using a few very precise physical laboratory experiments whose data were then greatly amplified using a computational method called combinatorics that tested thousands of combinations of cement composites and their photocatalytic qualities.
The results, say the researchers from C-Crete Technologies and Rice University, indicate that the ingredients themselves are more important than the molecular structure of the cement or the particle size of the photocatalyst used. This research offers not only an important finding for cement—as the need to make concrete and its primary ingredient, cement, more eco-friendly is a goal of much ongoing research—but the methodology holds promise for developing other environmentally friendly, multifunctional materials.
The findings could be applied in cement used in "roadways, bayous, canals, parking lots, anywhere that water washing over concrete's surface is exposed to sun," says Rouzbeh Shahsavari, president of C-Crete Technologies, lead author of the paper that appeared online April 27 in the journal Langmuir. "Since experiments are typically costly, difficult and time consuming, the exciting part of this work is that we can now analyze limited experimental results with our novel combinatorial approach and still obtain meaningful insights and correlations that would have been conventionally obtained by hundreds or thousands of experiments."
"Broadly, this method can be applied to not just cements or water purification applications but other areas in materials discovery that face limited and sparse experimental data. We have developed a platform technology that helps development teams to decrease the costs of their R&D and come up with completely novel materials with unprecedented and multifunctional properties." says Shahsavari.
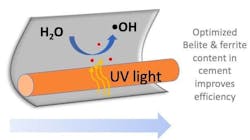
The researchers used five types of readily available cement, nine types of the photocatalyst titanium dioxide and two common pollutants—methyl orange, a cancer-causing substance, and dioxane, a possible carcinogenic compound—both of which are commonly found in drinking water. Of the five cements, White Portland Cement, two types of volcanic ash-based Portland Cements, and a commercially available photo-active cement all proved to have the replenishable photocatalytic quality. The most common cement, ordinary Portland Cement, did not.
"Basically, tweaking cement composition including its belite and ferrite will go a long way for photocatalysis while the mechanical properties remain essentially unchanged. " says Shahsavari.
Source: C-CRETE/EurekAlert