Factors to Consider when Purchasing Pump Parts
By Allan R. Budris
When a pump needs repair, or spare parts are to be purchased, there are often potential short-term cost savings, and possible delivery advantages, to buying Non-OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) repair parts. In addition, the water or sewage facility may have a well equipped machine shop that can fabricate various pump parts. Some do so effectively and save money in the process, while other facilities do so ineffectively and fare poorly in terms of pump MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures), pump life cycle costs and plant reliability.
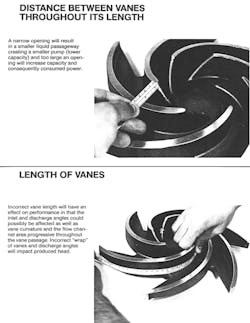
Figure 1: Some Critical Impeller Dimensions
Buying pump spare or repair parts on the basis of cost and delivery alone is normally not the best approach for reliability focused pump users. There are critical functional factors to consider, other than price and delivery, when making the decision on whether to purchase OEM or non-OEM parts. They are:
- The use of non-OEM parts may affect the manufacturer's warranty.
- Non-OEM parts may not meet OEM performance specifications. Proper impeller vane contours are difficult to copy, and subtle changes can have a substantial effect on pump performance.
- Since non-OEM parts are often copied from worn OEM Parts, critical fits and tolerances on copied parts may not meet OEM specifications, which can lead to premature failures. For example, if a shaft fillet radius is too small, it will increase the shaft stress concentration and could lead to a fatigue failure. If a shaft fillet radius is too large, it may interfere with proper assembly stack up. Machining marks under a shaft lip seal may cause it to leak in operation. Oversized ball bearing fits on the shaft can cause excessive pre-loads which drastically shorten bearing life.
- Non-OEMs do not have R&D facilities, so they cannot keep up with the latest part changes (mechanical, metallurgical and hydraulic improvements).
- Most pump OEMs meet ISP 9001 quality control standards, while non-OEMs cannot meet these requirements without OEM drawings.
- Metallurgies and material mechanical properties may not meet OEM specifications, possibly increasing corrosion rates or reducing pressure ratings.
There are also non-functional advantages to using OEMs, or their authorized distributors, for repair parts:
- Many non-OEMs only offer the most popular repair parts, so that users will still have to deal with OEMs for low volume parts. This sometimes causes the user to miss out on OEM quantity discounts.
- OEMs can offer application expertise, upgrade recommendations and recommended spare parts lists.
Pump Impellers
Impeller vane length, discharge and inlet throat areas, discharge vane tip thickness and discharge vane angle will affect developed head, pump efficiency and possibly the pump NPSHR. Even the way an impeller is deburred and/or balanced can affect pump head and efficiency. The height and angle of the pump-out vanes can affect axial thrust, hence, bearing life, and pump efficiency. Even the stuffing box pressure may be influenced by incorrect height (hence clearance) of back pump-out vanes. Finally, impeller bore tolerance and balance will affect pump vibration and mechanical seal life.
Too thin a vane will reduce its mechanical strength and enlarge the effective flow passageway causing increased flow and horsepower consumption, and too thick a vane will result in a reduced opening between vanes, creating a smaller liquid passageway and an effectively smaller pump (see figure 1). Bumps or irregularities along the vane surface, resulting from improper segmented pattern removal, can cause internal vortices which will block the flow and reduce capacity.
Pump Shaft
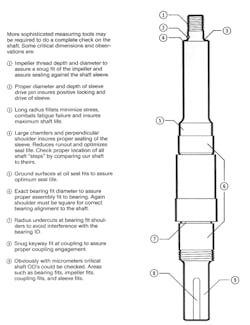
Shafts that are not machined to intended dimensions and tolerances can fail prematurely, reduce ball bearing life, reduce lip seal life, and/or increase vibration. Large radius fillets minimize shaft stress, which reduces the risk of fatigue failures and ensures maximum shaft life (see figure 2). Radius undercuts at bearing fit shoulders avoid interference with the bearing I.D., but again must be avoided in instances where the resulting stress riser effect would mandate de-rating the allowable torque input. Machining marks, inadequate surface smoothness and wear tracks can cause seal leakage. Here, too, experience-based decisions are needed.
Checklist
The following checklist items should be consulted before making critical repair part sourcing decisions:
- Will it affect the warranty & increase liability?
- Does the vendor maintain precise fits?
- Are parts imprecise copies of the OEM parts?
- Do the parts contain the latest design changes?
- Is the metallurgy the same as used for the OEM parts?
- Can the supplier ship parts the same day?
- Can the supplier offer application expertise to solve pump problems, and possibly avoid future failures?
- Lastly, what are the cost and delivery for the part(s).
Reference:
- Allan R. Budris & Heinz P. Bloch, "Pump User's Handbook – Life Extension, Second Edition, The Fairmont press, Inc., 2006 WW
About the Author:
Allan R. Budris, P.E., is an independent consulting engineer who specializes in training, failure analysis, troubleshooting, reliability, efficiency audits and litigation support on pumps and pumping systems. With offices in Washington, NJ, he can be contacted via e-mail at [email protected].
More WaterWorld Current Issue Articles
More WaterWorld Archives Issue Articles