New remediation technologies remove 99% of explosive organic compounds
By Daniel Billet
MPP technology removes dispersed and dissolved pollutants, helping industry to recycle and reuse waste and process waters, and remediate contaminated groundwater.
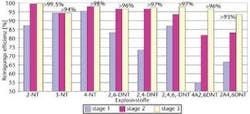
Field tests demonstrated that the Macro Porous Polymer Extraction (MPPE) process in combination with the Mixing Extraction Coalescing and Separation (MECS) process, both developed by Akzo Nobel Chemicals, can remove 99% of explosive organic compounds detected in groundwater on a former military site in Stadtallendorf, Germany. During World War II, more than 2,000 sites in Germany were used by the military to store explosives, including DNT and TNT. Consequently, explosive compounds contaminated soil and groundwater at many sites. The German Ministry for Environment has funded these field tests, which are still in the evaluation phase.
The subsurface remediation field demonstration using multistage separator and distillation (MECS) and MPPE technology treated water loaded with nitro toluene. The overall project goal was to remove 90% of the explosive substances from groundwater, but subsequent commercial units and field tests show that more than 99.99% removal efficiencies can be obtained.
The MPPE technology removes dispersed and dissolved pollutants such as aromatics, aliphatics, poly aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons to below one parts per billion. This process helps industry to recycle and reuse waste and process waters, and remediate groundwater. Pre-certified as a Best Available Technique, the technology requires low energy and no chemicals, and does not involve any air emissions or biological sludge formation.
Currently, 20 units are operational or under construction in the USA and Europe, of which ten treat process water and ten are used to remediate groundwater. Removal efficiencies up to 99.999% are achieved for a wide variety and combinations of aliphatic, aromatic and halogenated hydrocarbons.
Several hundred thousand polluted sites can be found worldwide, a situation that has prompted many countries to promote stricter environmental guidelines and regulations. More than 3,000 contaminated sites exist in France, according to the BASOL database. The French Ministry for Environment initiated this database in 2000. It provides a complete inventory of polluted sites in France and gives access to everyone who wants to learn more about characteristics of the pollution of a specific site, administrative actions and methods used for soil and groundwater remediation. Web address is: http://basol.environnement.gouv.fr/. Each district environmental agency "DRIRE" has the responsibility to keep it up to date with all actions taken by the owners about soil and groundwater remediation.
Industry must take informed action to prevent and remediate surface and groundwater pollution. Article 4 of the European Union's Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC) says that "Member States shall protect, enhance and restore all bodies of groundwater, ensure a balance between abstraction and recharge of groundwater, with the aim of achieving good groundwater status at the latest 15 years after the date of entry into force of this directive."
Manufacturing companies must operate in an extremely competitive environment where optimum use of capital and assets, in addition to low remediation costs, is the key to survival. Sometimes they are obliged to reallocate their production and to conduct a risk assessment study with the conclusion to operate site remediation. Manufacturing companies are looking for the best practices in order to achieve desired results in terms of complying with statutory requirements. Site remediation is becoming a key factor for all acquisitions.
How it works
MPPE uses two proven technologies: liquid-liquid extraction and steam stripping with an innovative medium (MPPE particles). Hydrocarbon contaminated water is passed through a column packed with MPPE particles.
An extraction liquid immobilised within the polymer matrix removes hydrocarbons from the water. Purified water passes out of the column directly for reuse or discharge. All hydrocarbons with a relatively high affinity for the extraction liquid (compared to water) are removed. Periodical in-situ regeneration (every two hours) of the extraction liquid containing MPPE particles is accomplished with low-pressure steam. The steam volatises the hydrocarbons. Volatised hydrocarbons and steam are condensed and then, the hydrocarbons are separated from the water by gravity. The hydrocarbon phase is recovered and sold as product; the water phase is recycled to the system. MPPE particle size ranges from 400 to 1,000 micron with pore sizes 0.1 to 10 micron. Resulting porosity is 70% to 80%.
The remote control facility with laptop and mobile telephone enable quick response, remote shut down/start up and adaptations of process conditions. Pre-filters are installed to avoid blockage of the MPPE bed due to the accumulation of solids in groundwater.
A computerised mathematical model is used to design a specific application. All relevant physical processes are taken into account:
•Liquid/liquid (extraction and vapour/liquid (regeneration equilibrium)
•Liquid/liquid and vapour/liquid mass transfer
•Residence time distribution in the MPPE bed
•Heat transfer (regeneration)
•Pressure drop over the packed bed (during extraction and regeneration)
•Units with flows up to 1200 m3/h have been offered.
A 50% higher influent concentration than designed can still be reduced to the required effluent concentration of 0.1 ppm with only a 10% flow reduction. A higher flow rate results in a higher effluent concentration. To return the effluent concentration back to design conditions is more difficult. Therefore, the unit should be designed with respect to the maximum expected flow and concentration, enabling higher flows and concentration to be treated.
The components that can be removed by the MPPE technique must have a high affinity (i.e. partition coefficient) for the extraction liquid compared to water in order to allow extraction, and a sufficient volatility to allow regeneration by steam stripping.
Project applications
In the Stadtallendorf project, water contaminated by nitro substances from recovery wells passed through a multistage separator and distillation called Mixing Extraction Coalescing and Separation system (MECS) before it was fed to the MPPE unit. Nitro compounds were removed from the toluene solution for safety reasons. Toluene can be removed easily from water with MPPE technology. The MECS unit size with steam generator was restricted to fit into a standard 20-feet treating groundwater (1 m3/h max flow). No production chemicals were used.
Akzo Nobel, in cooperation with the German Frauen Hofer Institute and the German Environmental Ministry, developed and patented MECS.
In Flensburg, Germany, aromatics (BTEX) and polyaromatics (PAHs) contaminated the groundwater at the site of a gasworks factory, the Stadtwerke Flensburg GmbH, from 1929 to 1963 when city gas was used. Several groundwater remediation technologies were studied before the MPPE unit was installed in 1998. In particular, air stripping with gas phase active carbon treatment and water phase active carbon treatment were evaluated for this specific project by the management of Stadtwerke Flensburg GmbH with a German environmental bureau.
On request of the NOGEPA, Stork Engineering Consultancy B.V. performed a study on techniques for reducing heavy metals and aromatic hydrocarbons emission on offshore locations. Out of 55, one of the most promising techniques was found to be the Macro Porous Polymer Extraction process of Akzo Nobel. The OSPAR (Oslo-Paris) Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Northeast Atlantic listed the MPPE technology as Best Available Technology (BAT) for oil and gas produced water.
Both required iron and manganese removal prior to the treatment train. MPPE did not have this disadvantage and proved technologically feasible and the least costly.
The unit treats six cubic metres per hour of contaminated groundwater. The influent concentration of the sum of BTEX and PAHS can be as high as 14 mg/l. The PAHs contribute approximately 4,000 ppb (80% naphthalene), while BTEX concentration can be as high as 10,000 ppb. Some analysis overviews of groundwater and treated water from this on-going project are available upon request. The MPPE unit consistently met effluent requirements to reduce compounds to less than 10 ppb in the last four years. Simultaneously, environmental guidelines and regulations have become more encompassing and progressively stricter in the field of offshore water treatment. TOTAL FINA ELF, NAM BV (JV Shell / Exxon; Shell-operated) , and STATOIL have shown a great interest in testing the applicability of MPPE (Macro Porous Polymer Extraction) technology on offshore-produced water and anticipate possible future legislation.
Author's note
Daniel Billet is the commercial director for Akzo Nobel Chemicals, based in Compiègne, France.