Helping India Power Ahead
India is building power plants at an incredible rate to keep pace with extreme demand for electricity. As the largest industrial user of water, such facilities need to implement modern technologies to keep water loss to a minimum. Govindan Alagappan, Thomas Bayer and Paresh Vora discuss water treatment technologies being used in the Indian power market.
India has the second largest population in the world. It is expected to surpass China this decade but it remains only the sixth largest energy consumer, accounting for 3.4% of global energy consumption. India requires electric power to close the demand supply gap caused by the growth rate of the economy. This means it is among the top countries building power plants today.
The single largest industrial user of water in India is power plants, and these plants consume roughly 90% of the water used by all the industries put together. Availability of water for power plant use is one of the key factors considered when choosing a location and securing commercial approval of new power plants. Because sustainability has become such an important topic, the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in India is turning its focus towards efficient and effective use of water in power plants.
Water treatment technology in power plants
Among the critical areas for water treatment and use in power plants are intake screening, the steam turbines cycle (boiler feed & condensate treatment) and the cooling water system. Intake screens work as a barrier at the intake structure to the seawater being used by the power plant, and also protect the intake structure, pumps and pipes from unwanted material. Failure of these screens may lead to reduced cooling water flows and damage to equipment. Feedwater is added to the steam boiler to replace evaporation and blowdown.
In many cases, condensed steam returned to the boiler through the condensate system provides much of the feedwater. Before use, this condensate must be purified or "polished" to remove impurities that could damage the boilers, steam generators, reactors and turbines. Both dissolved (such as silica oxides) and suspended matter (such as iron oxide particulate), as well as other contaminants that can cause corrosion and maintenance issues, are effectively removed by condensate polishing equipment.
Cooling towers cool the recirculating water in a system through the evaporation of the water. Evaporation concentrates the dissolved and suspended solids in the cooling water, leading to the potential for scaling and solids buildup in the cooling tower and cooling circuit. To avoid these problems, the make-up water to the cooling tower must be treated and a small amount continuously purged to prevent scaling and solids build-up in the cooling tower. Cooling tower make-up water is treated to remove hardness, silica, suspended solids, and in some cases, organics.
Intake Screening Technologies
Water screens for power plants need to survive the extremely corrosive environment and it is important for power producers to consider the screen's design. Traveling water screens take many forms, from simple to more sophisticated automated screens that have self cleaning features. Some are designed as coarse screens for removing large floating debris like sticks, trash and plastic; fine screens are able to remove finer suspended materials. Some are configured to safely prevent fish from entering water intake systems.
Boiler Feedwater Treatment Technologies
Power plants use deionized water as make-up to high pressure boilers, for producing steam to drive turbines and generate electricity. The quality of the boiler feedwater depends on the boiler type and pressure. Any hardness contaminants can precipitate directly on the boiler and form scale, which affects the performance. The conventional means of purifying boiler feed water has been to use clarification and filtration processes to treat the raw water for removal of physical impurities, and chemically regenerated ion-exchange deionization for the removal of dissolved ions.
Over the past decade, the global power industry has witnessed a technology shift in the entire boiler feed water treatment. Ultrafiltration (UF) membranes are used as a physical and verifiable barrier to remove suspended solids, which protects and extends the life of the downstream equipment and also accounts for the seasonal changes and variations in source water. Secondly, reverse osmosis (RO) is used as a roughing demineralizer to remove the bulk of the mineral, organic and particulate contaminants and reduce the chemical consumption of the polishing ion exchangers. Improvements in electrodeionization technology have caused a movement towards chemical-free deionization systems.
Condensate Polishing Technology
Condensate polishing treatment is a key technology required for the recycling of the condensed water within the steam turbine loop.
After driving the turbines, the steam flows to condensers. The condensed water picks up some corrossive products during the passage through feed water pumps, piping, steam turbine loop (including boiler) and the condenser. These impurities can affect the boiler and also impact the life of the turbine. Condensate polishers save power utilities money through a reduction in facility start-up times, thereby saving fuel and direct labor and minimising blowdown.
This polishing can be accomplished with a mixed bed ion exchange system that uses both cation and anion bead resins. Certain deep-bed condensate polishers use strong-acid and strong-base resins to produce a very high quality demineralized water. They are typically used in applications where the feedwater contains low levels of Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) and where the power plant may have minor condenser leaks.
Such systems involve several vessels operating in parallel. When the mixed-bed resin capacity is depleted, the "spent" resin is transferred to an external system for separation, backwashing and regeneration.
The external regeneration process avoids cross contamination of resins with the regenerant chemicals, and therefore prevents them from accidentally entering into the boiler. The key to the success of the condensate polishing unit (CPU) is the separation of the cation and anion resins before regeneration.
When a leading Korean contractor wanted demineralization equipment and a condensate polishing system for a project in Saudi Arabia, Siemens supplied three mixed-bed demineralizer systems and four high-pressure spherical condensate polishers with the Fullsep external regeneration system. The mixed-bed systems will be used to polish desalinated water from the Red Sea to boiler feedwater quality. The condensate polishers will remove impurities such as metal oxides, trace ionic contaminants and silica from the condensate cycle to maximize water use, bring the power unit online faster, reduce operating and maintenance costs for generation assets, and improve and maintain boiler chemistry.
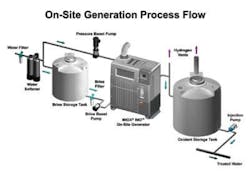
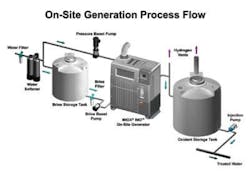
The micro and macro fouling in the cooling water circuit affects the heat transfer efficiency in the power plant condenser tubes, which in turn affect the overall power plant efficiency. This fouling is avoided using chlorination of the cooling water, which can be accomplished by using electrochlorination technology.
Moving forward, with India as one of the top countries building power plants, it will need dependable and sustainable water treatment technologies with low lifecycle costs now, and in the future.
Author's note: Paresh Vora is based at Siemens Water Technologies in India, Govindan Alagappan is regional sales manager for process water solutions at Siemens Water Technologies and Thomas Bayer is sales director for Chloropac Systems at Siemens Water Technologies, based in New Jersey, U.S.A. They can be contacted at: [email protected], [email protected] and [email protected].
More Water & WasteWater International Current Issue Articles
More Water & WasteWater International Archives Issue Articles