Benchmarking: Water and Wastewater Energy Efficiency
By Stefania Galletti and Dave Landon
WRc plc, a UK consultancy offering services in the water, waste and environment sectors, is coordinating an international program on Energy Efficiency Benchmarking addressed to water and wastewater services operators.
The program, which started in 2006, currently involves nine water utilities including four based in the UK, four in Italy and one in Ireland. It is designed to help utilities identify areas where they can save energy, monitor improvements in energy use resulting from process changes, and identify and share Best Practice with others.
WRc is actively seeking additional utilities to participate in the program.
It is important to note that the program focuses upon electricity consumption reduction, not on the comparison of electricity costs as these can be based on different prices across different geographical areas. However, one of the most relevant objectives of the program is the reduction of energy costs.
Following initial phases to investigate advanced energy benchmarking techniques, to develop a web-based software, and to define a Best Practice Methodology, the program is now fully operating and has been rolled out to permit participants to model any water or wastewater treatment works of their choice.
The program's main objective is to provide an answer to the following questions:
• Energy: how much are we using, where are we using it and how do we compare with each other?
• What is the benchmark for energy efficient treatment?
• What can be reasonably achieved in terms of further efficiencies on a site-specific basis?
Both in water supply and wastewater treatment, electricity consumption is the greatest element of operational costs. The ever-rising price of electricity and concerns over global warming reinforce the need to understand whether electricity is used efficiently, to be able to locate possible inefficiencies and plan for effective interventions where energy use can be reasonably reduced without compromising performance.
In order to effectively manage electricity use at treatment works and in the distribution network, consistent and tailored monitoring of consumption is the key starting point, followed by an analysis of meter readings (or electricity estimates if readings are not available), eventually leading to the identification of problematic areas. The choice of follow-up actions or an intervention plan, when needed, is greatly assisted by a benchmarking exercise, both internally and with external operators, as well as by discussions, sharing of experiences and know-how on relevant topics.
Each of the stages just described has been considered during the development of the WRc Energy Efficiency Benchmarking Program and the creation of its web-based software EnergyPI, which can be found at www.energypi.com. While full access and use of the software are restricted to those water utilities taking part in the program, some general information on the project has been made available on the website.
For each works entered, the software EnergyPI allows the user to:
1. Create the treatment works "schematic", a simplified graphical model;
2. Enter the works static data (Population Equivalent - PE, load, flow rate, etc.) and static data of each individual process identified in the works schematic;
3. Upload time series (primarily flow rates, electricity consumption – meter readings or estimated – and physical/chemical data) for the whole site as well as each single process;
4. Run the calculations, which provide specific efficiency parameters entitled Energy Performance Indicators (EPIs);
5. Display the results through a choice of outputs which include detailed routine reports, monthly reports of EPIs for the site and its individual processes, and comparison graphs showing a site's performance in terms of electricity use against the performance of similar sites modeled in the software. The comparison can be carried out between sites of the same utility or sites of the other participating companies, on an anonymous basis.
Both the assessment of efficient performance and the benchmarking exercise are based on the definition of EPIs. These are efficiency parameters, selected by the project liaison group and implemented in the model's calculations. Using the data entered and uploaded by the user, the software provides a variety of actual and theoretical EPIs. The respective values are compared and evaluated to determine how efficiently the electricity is used at a works, or by an individual process. The comparison is expanded to the processes and/or works of the other participants, with the facility to select other works with similar size and effluent characteristics. When the output suggests that electricity is used inefficiently, "explanatory factors" are automatically flagged. Operational adjustments or intervention plans may then be recommended.
As an example, the formula below refers to the actual EPI of a pump, expressed in kWh/Megalitre of flow volume:
The pump's actual EPI is compared with the theoretical (or ideal) EPI, calculated from the pump's parameters through the following formula:
where: Energy unit conversion: 1 kWh = 3.6 MJ;
the pump head is expressed in m;
the efficiency is a percentage (%).
Similar equations have been implemented in the software for all common treatment processes and for the site as a whole. The comparison between actual and theoretical EPIs allows the user to make an informed and rational decision aimed at identifying possibilities of improvement.
WRc plays an ongoing role in guiding the participating utilities in modeling strategy, providing user support in creation of models, understanding the output and facilitating collaboration between participants. Meetings are held twice a year to facilitate discussion and share experiences and initiatives among the participants, as well as investigate new ideas and technologies. This leads to a better understanding by participants of the Best Practice Methodology.
The performance assessment and benchmarking become even more significant and useful as more participants join the program. The software website provides an area for discussion where users can interact and share information and experiences on energy saving initiatives, especially between the project meetings. Actively participating in the program also provides a means to monitoring the effects of energy saving initiatives, and to learn from the experiences of other participants.
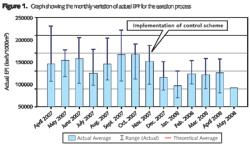
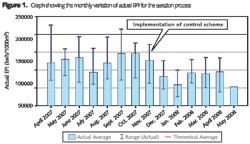
The graph in Figure 2, a screen shot from the EnergyPI software, illustrates such benefits.
The graph refers to a wastewater treatment works with PE of 90,000. The operator has used the EnergyPI software to monitor the effects of an initiative on aeration control in an activated sludge tank. Electricity savings up to 2,000 kWh/day have been achieved since implementation of the scheme (Nov 2007). The user has also used the software to monitor further improvements by adjusting the algorithm of the aeration control device. This scheme has been presented by the operator at WRc and discussed with the other participants, who have been able to estimate the level of electricity savings that the application could determine at their own wastewater treatment sites.
Energy and R&D Managers of the participating companies are now actively monitoring some of their water and wastewater treatment sites. The objective is to be able to identify where electricity is used inefficiently and what can be done to cut consumption and associated costs, and therefore also reduce CO2 emissions from operational activities.
For further information on the EnergyPI software, please contact: [email protected] or Amanda Burch (Business Development Manager) at +44 (0) 1793 865086.
More Water & WasteWater International Current Issue Articles
More Water & WasteWater International Archives Issue Articles