MBR Still Growing in EU Wastewater Treatment Market
With less than 100 membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems installed in 2000, Europe now boasts over 350 employed in municipal and industrial wastewater applications and projected annual market growth of 7.9%, according to new research from Frost & Sullivan.
By Jaishri Srinivasan
Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) are a relatively new technology which combines several typical unit operations – primary sedimentation, activated sludge aeration and sedimentation, and tertiary media filtration – into a single treatment step. MBR has great potential in wide ranging applications including municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, solid waste digestion and odour control. Full-scale systems are operational worldwide and the list of installations continues to increase at a relatively rapid rate compared to conventional treatment solutions.
The economics of MBR technology rests on four main factors: 1) relatively high capital costs, 2) energy consumption, 3) membrane lifecycle costs, and 4) filtration rates.
Energy consumption in MBR plants is higher than in conventional plants due to additional energy requirements during operation, mainly during air scouring of membranes. Differences in module design could affect the efficiency of aeration. The development and successful commercialization of the technology has led to an appreciable decline in capital and operating costs. But the high energy costs remain a concern.
A Global Overview
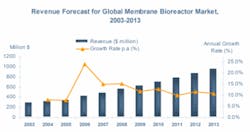
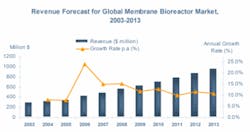
Frost & Sullivan estimates the global MBR market to be worth $420.9 million in 2006 with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 12.5%. The European market, continues to be one of the significant markets and accounts for a 21% share of the total MBR market.
Key drivers in the worldwide market boil down to two main categories – legislation to curb water pollution and water scarcity prompting the need for wastewater recycling. Some of the current applications include water recycling in buildings, municipal wastewater treatment for small communities, industrial wastewater treatment and landfill leachate treatment. Other potential areas MBRs could be used, that have been little explored, include treatment of wastes generated from agricultural sources and livestock operations, wastewater originating from food processing industries, removal of herbicides and pesticides and biological nitrate removal. Sports stadiums, shopping complexes and office blocks are becoming typical end users, especially in areas of water stress.
null
EU Drives & Challenges
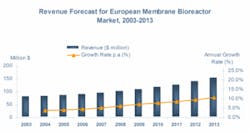
Frost & Sullivan estimates the European MBR market at $90.4 million in 2006 with a CAGR of 7.9% until 2013. One key trend driving this growth is increasing use of MBR systems for decentralized treatment and water reuse. The market is characterised by medium- and small-sized municipal and industrial MBR systems with a few rare exceptions that are large-scale plants.
Since 1999, Zenon and Kubota have been leading the implementation of large- and medium-scale MBRs for municipal wastewater treatment in the UK, Germany, France, Italy, the Netherlands and Spain among other countries. The split between the two broad end-users in the European MBR market is estimated to be 41% for the industrial sector and 59% for the municipal sector.
The Northern European MBR market is dominated by activity in the municipal sector in the UK and Ireland primarily, while Germany and the Benelux region display more demand for MBR systems from the industrial sector. This region dominates the overall European MBR market with a revenue share of 50%.
The Southern European MBR market is experiencing relatively higher annual growth rates and, by 2013, it’s estimated to have a revenue share of 43% of the total European market. The dominant driver for this region is water scarcity prompting a need for wastewater recycling.
Eastern Europe is a growing market. Its first full-scale commercial MBR was installed in Hungary in 2003. This number has doubled over and over in subsequent years until 2005, when a couple of municipal MBR plants were commissioned, too. There are now 10 MBR plants in Hungary, four of them municipal plants. Poland is a growing market that only came online with MBR systems since 2006.
Traditionally, although Scandinavia has been the home of advanced wastewater and sludge treatment systems, acceptance of MBR has lagged with virtually zero penetration in this region. Apart from a few small systems installed by Kubota, there hasn’t been any activity in the region. This is expected to change as more companies tap into the market for small and discrete MBR systems and packaged solutions more suited for this market. Stockholm-based Alfa Laval has launched its own MBR system and is set to tap into the potential profits.
Accession to the European Union also has catalysed MBR opportunities in countries such as Cyprus, which recently joined and is the focus of significant investment in water and wastewater treatment infrastructure upgrades. The high degree of freshwater stress has benefited water reuse and recycling solutions and there are already three MBR systems slated for commissioning through 2008. Two of these are of significant capacity, 13,000 m3/day and 14,000 m3/day.
Among the Alpine countries of Austria and Switzerland, apart from a medium-sized industrial and municipal MBR system installed respectively, there are limited opportunities in this saturated market unless demand arises for small household wastewater treatment systems in remote areas.
With respect to Chart 1, Northern Europe comprises UK & Ireland, Germany, Benelux (Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg), Austria, Switzerland and Scandinavia. Southern Europe includes France, Italy, Iberia, Greece and Cyprus. Eastern Europe includes Poland and Hungary at present.
The number of discrete and small systems is growing and this trend is expected to be driven by the following factors:
- Experience gained with pilot/small-scale projects,
- Drastic decrease in the cost of membranes,
- Availability of subsidies,
- Small footprint and small reactor volume,
- Development of guarantees on membrane life spans and of maintenance contracts.
MBR markets have received a huge boost in the municipal segment with legislative drivers such as the Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive (UWWTD) requiring lower nutrient discharge limits. The ceiling for discharge is even more severe in the designated “Sensitive Areas” and improvements in membrane performance have resulted in high treatment efficiencies with MBR use. MBR also gains an edge over conventional systems with its ability to substantially reduce the amount of sludge generated.
Implementation of Integrated Pollution Prevention Control (IPPC) policies have catalysed growth of the MBR markets for the industrial sector. The major industrial end-user is the food & beverage sector, with pharmaceutical, tank cleaning, textile, petrochemical and other industrial sectors also sporting MBR systems. The largest industrial MBR system in Europe in terms of installed capacity is currently installed at a petrochemical facility in Italy, with a capacity of 47,420 m3/day. Also there’s an increasing trend toward use of MBRs to treat difficult wastewater such as landfill leachate treatment applications.
Still, there are a few drawbacks which continue to pose challenges to the takeoff of MBR technology:
- Capital intensive compared to conventional treatment systems although the gap has been consistently closing.
- More automation required, not only in design and start-up but also in ensuring daily operational optimization and drive home the advantages compared to a conventional activated sludge system.
- Biofouling, which increases operating pressure, reduces maximum flux, increases recovery cleaning requirements and possibly reduces total membrane life.
- Membrane strength still remains an element of concern.
Moreover, although the cost of membrane processes has dropped by up to 30-fold since 1990, MBRs haven’t been operational long enough to have data on membrane life – so this cost is unknown. The European Commission has initiated development of MBR technology by funding four projects involving research, development, capacity building and technological transfer:
- AMEDEUS – Accelerate Membrane Development for Urban Sewage Purification.
- EUROMBRA – MBR with an EU perspective for advanced municipal wastewater treatment strategies for the 21st century.
- MBR-TRAIN – Process optimization and fouling control in MBRs for wastewater and drinking water treatment.
- PURATREAT – New energy efficient approach to the operation of MBRs for decentralized wastewater treatment.
Around 50 European and international companies and institutions are actively involved in these four projects and have joined their efforts within the MBR-Network. As a couple of the programs such as AMEDEUS and EUROMBRA are set to be completed late next year, there arise possibilities of commercialization of the research undertaken toward optimization of the MBR technology and process. This will further boost the European MBR market at a significant pace, though to match the high pace in the fast growing regional markets of the Asia-Pacific and Middle East would be difficult.
Conclusion
There appears to be a considerable risk that EU subsidies will lead to excess investment in sewage treatment plant capacity. The right balance between achieving high water quality standards and adequate sewage treatment capacity needs to be found. MBR systems appear to address this very well indeed and it’s a sure path to attain water sustainability in the municipal sector and more importantly in the industrial sector.
MBR technology has set a sound foundation and is constantly strengthening its credentials to fuel overall growth in the European market. Underlying engineering principles are well-recognized and have been instrumental in success of many applications to verify performance efficiency and identify critical design and operating factors. Furthermore, commercial availability of the technology with an attractive pay-back period, especially in some key industrial sectors, implies it’s set to tap into existing and developing demand backed up by relevant legislation, reliable equipment and technological support.
Author’s Note:
Jaishri Srinivasan is a senior research analyst for Environment & Building Technologies at Frost & Sullivan, with headquarters in San Antonio, Texas, USA. She’s based in its London office. Contact: +44 (0) 20 7730 3438 or www.environmental.frost.com
Cartridge filter market to grow 40% over five years
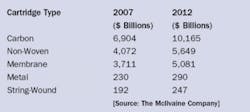
Membranes are third behind carbon and non-woven segments of the cartridge liquid filtration market, which will climb to $21 billion in 2012 from $15 billion in 2007, according to the latest forecasts in the continually updated McIlvaine online report, “Cartridge Filters: World Markets”.
With over 10,000 companies manufacturing cartridge filters worldwide, the residential market in Asia will lead the way with growth to over $2 billion by 2012 – up $700,000 from this year; and an office building boom that will spur the commercial institutional segment to more than triple to $1.3 billion by 2012.
Membrane cartridges, used in healthcare, pharmaceutical, semiconductor and other applications where ultra-pure water is needed, will see strong growth. Micro- and nano-fiber advances are driving improvements in non-woven cartridges, with strengths cited in chemicals, food and healthcare. Carbon filters that improve taste are heavily used in commercial and residential applications, such as refrigerators, soft drink machines and household filters. And industrial companies are finding increasing value in this cartridge type.
Earlier this year, another McIlvaine online report on, “RO/UF/MF World Markets”, pointed to a spurt in consumer and industrial demand for cross-flow membrane systems and replacement membranes to over $11 billion in 2011, up from $8.3 billion in 2007.
The most efficient membrane, which removes salts and the finest particles, reverse osmosis (RO) represents 45% of total sales. Ultrafiltration (UF) and nanofiltration (NF) account for 20%.
Microfiltration accounts for 30% and is less efficient than the other membranes, but nevertheless does remove sub-micron particles.
Improved production and technological advances make membrane costs comparable to multimedia filtration, the workhorse of municipal water filtration, while offering greater filtration efficiencies. With unreliable water supplies in many countries, the explosive growth in bottled water consumption in developing nations also contributes to membrane sales growth.
Industrial high-purity needs such as ethanol plants, which employ membranes for high quality boiler feed water and other applications, also are driving the market. U.S. ethanol use is expected to nearly quintuple to 120 billion gallons a year to reach a target of 20% of transportation fuels. Brazil is another big ethanol market and China has initiated an aggressive program as well.
The largest membrane application, desalination – which accounts for over 20% – will see its share rise above $2.5 billion in 2011. In the Mid-East, this is growing at 7% a year, led by activities in Saudi Arabia.
McIlvaine Company
Northfield, Illinois, USA
Enquiry No. XXX
Korean semiconductor plant buys membrane contactor
A Liqui-Cel® Membrane Contactor system for oxygen removal from Membrana is being shipped to Korea. The 130 m3/hr (572 gpm) system, which will operate in combo mode using nitrogen and vacuum, utilizes Liqui-Cel 10 x 28 Membrane Contactors to provide a dissolved oxygen outlet of no greater than 1 ppb. The Korean plant manufactures semiconductors used in electronics and pharmaceutical device applications. The Liqui-Cel contactors were chosen due to long-term success in high purity applications and because of their modular nature and cost effectiveness.
Membrana GmbH Wuppertal,
Germany Enquiry No. XXX
Two companies earn GE ecomagination awards
GE Water & Process Technologies honored German water management group Erftverband with a global ecomagination Leadership Award for its role in improving environmental, public health, and aesthetic water qualities of the Nordkanal. For nearly four years, Erftverband has used GE’s ecomagination-certified ZeeWeed MBR technology at the Kaarst Wastewater Treatment Plant in North Rhine Westphalia, which serves a population of 80,000. Treated effluent from the system is discharged to the Nordkanal, and can contribute as much as 50% of the flow to this sensitive, slow moving waterway that’s highly susceptible to pollutants. Once the system replaced the city’s 30-year old conventional treatment plant, the waterway experienced continuously rising water quality and aquatic health. USA-based Archer Daniels Midland also earned an award for its Decatur, Illinois, corn plant, which processes corn for food, feed, industrial products, and biofuel, and implemented a sustainable water management program – conserving 150 million gallons of water a year and realizing $1 million in annual operational savings over the past decade with ZeeWeed technology.
GE Water & Process Technologies
Trevose, Pennsylvania, USA
Enquiry No. XXX
Siemens, inge AG to cooperate on UF filter
inge AG, of Greifenberg, Germany, has granted exclusive rights to Siemens Water Technologies to supply and distribute its dizzer ultrafilter membrane modules in the Americas, Australia, New Zealand and the United Kingdom. Now, along with its Memcor membrane product line, Siemens is a global leader and the only manufacturer and system integrator of both submerged and pressurized low-pressure membrane products. These systems are used for applications covering drinking water treatment, municipal and industrial
wastewater treatment, and pretreatment in reverse osmosis.
Siemens Water Technologies,
Erlangen, Germany
Enquiry No. XXX